Advances in Technology Anti-Counterfeiting
Advances in Technology Anti-Counterfeiting
With the widespread use of anti-counterfeiting holograms and security labels, fake ID card manufacturers have adopted high-quality holographic foil materials and laser engraving technology to replicate the authentic appearance of these features. How this benefits fake ID production:
Holographic foil materials: Ohio fake ID card producers now use advanced holographic foils that closely resemble the foils used in official documents. These materials can replicate the reflective properties and multi-dimensional effects found on real security holograms, making it difficult for the untrained eye to distinguish between genuine and fake holograms.
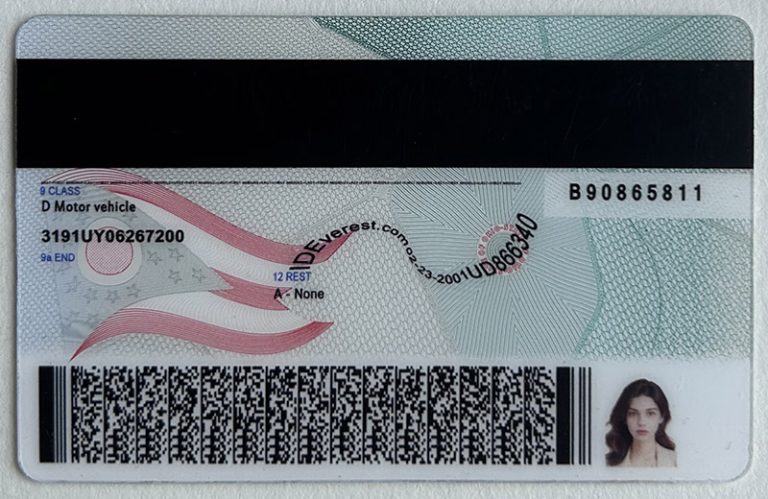
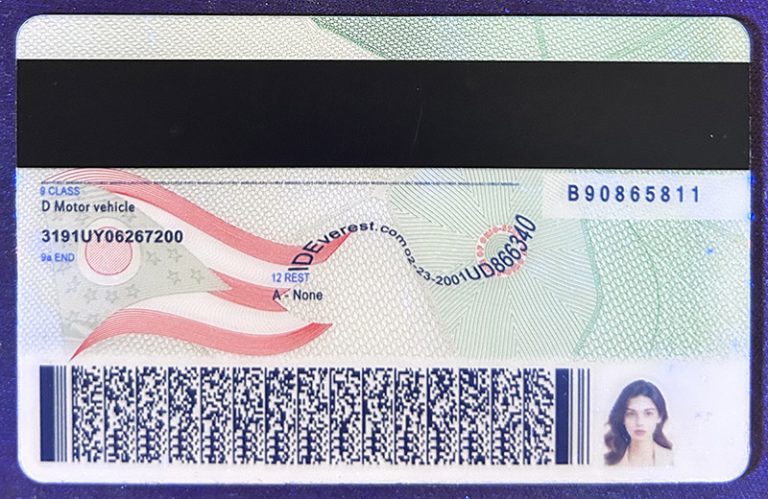




Laser engraving fine details: Laser engraving technology can accurately reproduce the complex holographic patterns and microtext found on real documents. This level of detail can mimic the layered effects of the original security features, increasing the credibility of fake ID cards.
3D visual effects: The ability to reproduce complex 3D visual effects, such as depth and motion, in holograms makes fake ID cards more convincing. These effects are often used as anti-counterfeiting measures for real ID cards, and replicating them helps North Carolina fake ID card suppliers produce products that pass visual inspection more effectively.




Overlay Technology: Some manufacturers also combine holograms with other security features, such as UV ink or microprinting, to better mimic the layered security methods found in real ID documents.
High-quality printing technology
The speed at which fake IDs are produced has greatly increased, improving the authenticity and effectiveness of these forged documents. Here’s how these technological advances benefit fake ID production in Illinois:Improved Resolution: Modern printers can produce resolutions in excess of 2,400 dpi (dots per inch), allowing for more accurate reproduction of fine details. This is critical for mimicking complex security features found on real IDs, such as microprinting and intricate background patterns. Higher resolution ensures that even the smallest text or graphics on an ID card look sharp and realistic.



Color Accuracy: High-quality printers can more accurately reproduce a wide range of colors. This is important because legitimate IDs often use unique hues, gradients, and color transitions as security features. Advanced printing technology allows fake ID manufacturers to closely match these color profiles, making forgeries more difficult to detect.
Specialty Inks and Printing Methods: Advanced printing techniques, such as UV ink printing and thermal printing, are now used to replicate features such as UV security markings and raised text. These techniques were once exclusive to governments or professional printers, but recent technological advances have made them available to counterfeiters, allowing them to create fake IDs with more sophisticated features. Enhanced durability through lamination: High-quality lamination and printing on durable plastic materials, such as polycarbonate, allows fake IDs to withstand wear and tear, making them feel similar to legitimate IDs. Using multi-layer printing and lamination techniques adds another layer of authenticity by mimicking the structural feel of real IDs.
Replicating security patterns: Technologies such as hologram replication and laser printing can recreate the complex visual effects used in legitimate ID security, including holographic overlays and color-shifting images. This advancement makes it difficult for the untrained eye to distinguish between a genuine Connecticut ID card and a fake one. Barcode and magnetic stripe programming has been a major advancement in fake ID manufacturing, increasing the usefulness and credibility of counterfeit IDs. Here’s how this technological development has benefited fake ID production:




Barcode encoding: Fake ID vendors can now program barcodes to contain encoded information that mimics real data, such as date of birth, name, and state ID number. By using specialized software, these barcodes can be scanned in venues such as clubs, bars, and retail stores, allowing fake IDs to pass basic electronic verification checks. This adds a layer of functionality beyond just a visual check.
Programming Magnetic Stripe Data: Similarly, magnetic stripes can encode personal information that mirrors the data on a real ID. With access to an encoding tool and blank magnetic stripe cards, counterfeiters can replicate the data in the same format as a real ID. This means that when a fake ID is swiped over a magnetic stripe reader, it can display valid data, making the forgery more difficult to detect. Enhanced Compatibility with Scanning Devices: Since many institutions and businesses use scanning devices to verify identities, fake IDs that can be electronically scanned can evade detection more effectively. By programming the barcode and magnetic stripe to contain credible information, these fake IDs can work with scanners used by point-of-sale systems, access control points, and age verification stations.
Integrating with Database Systems: In some cases, vendors can program IDs to mimic data formats that are compatible with government or commercial databases, making the counterfeit ID more convincing when scanned or swiped.
Fake ID manufacturers have improved their techniques by replicating the high-quality materials and multi-layered construction used in legitimate IDs:
Copycat Polycarbonate Plastic: Genuine IDs are often made of durable materials, such as polycarbonate plastic, which is resistant to wear and tear. Fake ID manufacturers replicate this material by using high-grade plastics to mimic the hard feel and weight of legitimate cards. This approach helps achieve a similar look and feel, making it more difficult to distinguish fake IDs from real ones just by touch.
Multi-Lamination Technology: Legitimate IDs often feature multiple layers of lamination to embed various security features, such as holograms, UV inks, and microtext. Fake ID producers have adapted this practice, utilizing similar lamination methods to replicate these layers. By laminating multiple layers together, counterfeiters can achieve the same visual depth and durability as a genuine card, which increases the credibility of the fake ID.
Incorporation of Security Elements: Some advanced fake IDs go a step further and embed security features similar to those found on legitimate polycarbonate cards, such as clear windows or tactile elements. While these features are often simpler than the originals, they can still fool basic inspection techniques. Matching Weight and Flexibility: Counterfeiters also take care to mimic the exact weight and flexibility of a real card. They do this by choosing materials that closely match the physical properties of the original, ensuring that the fake ID feels authentic when held in the hand.




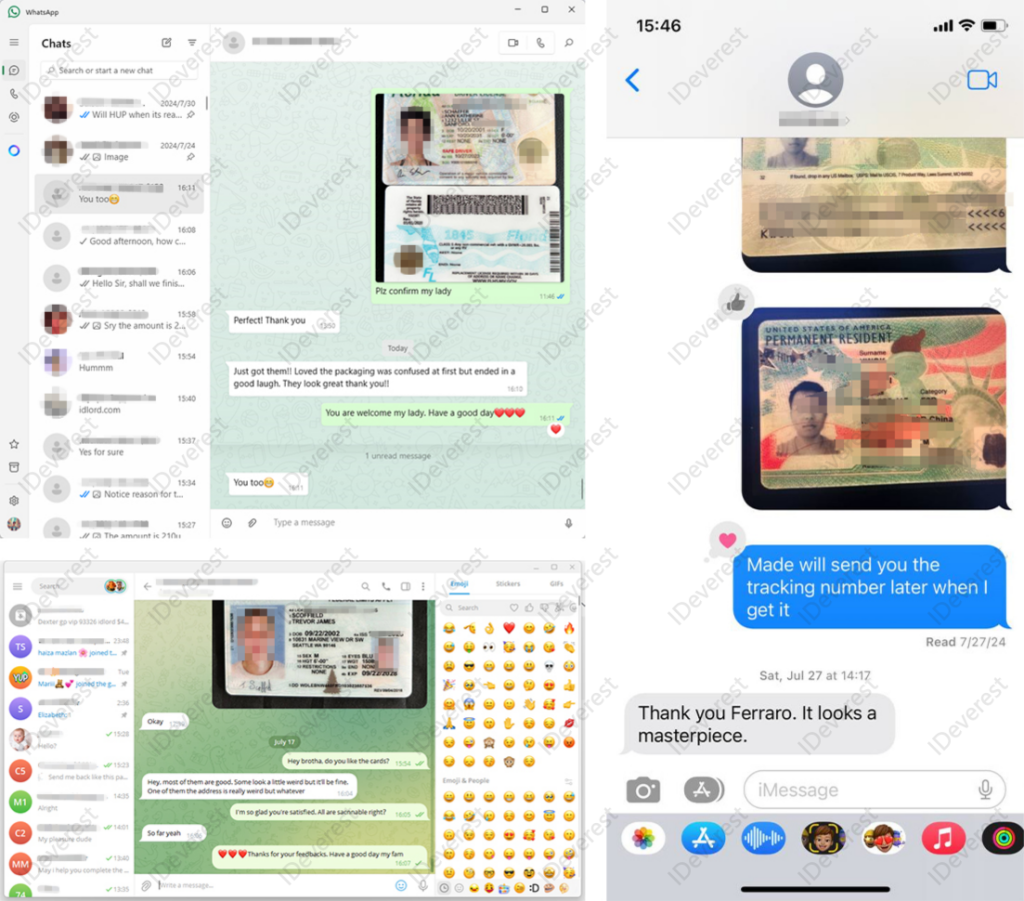
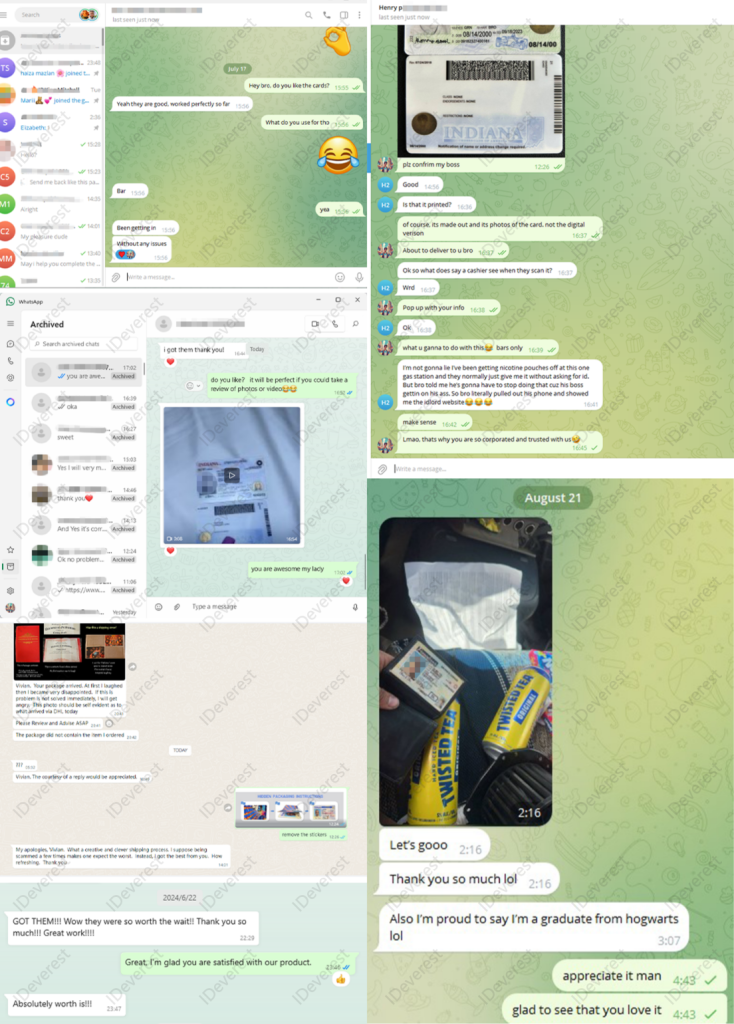
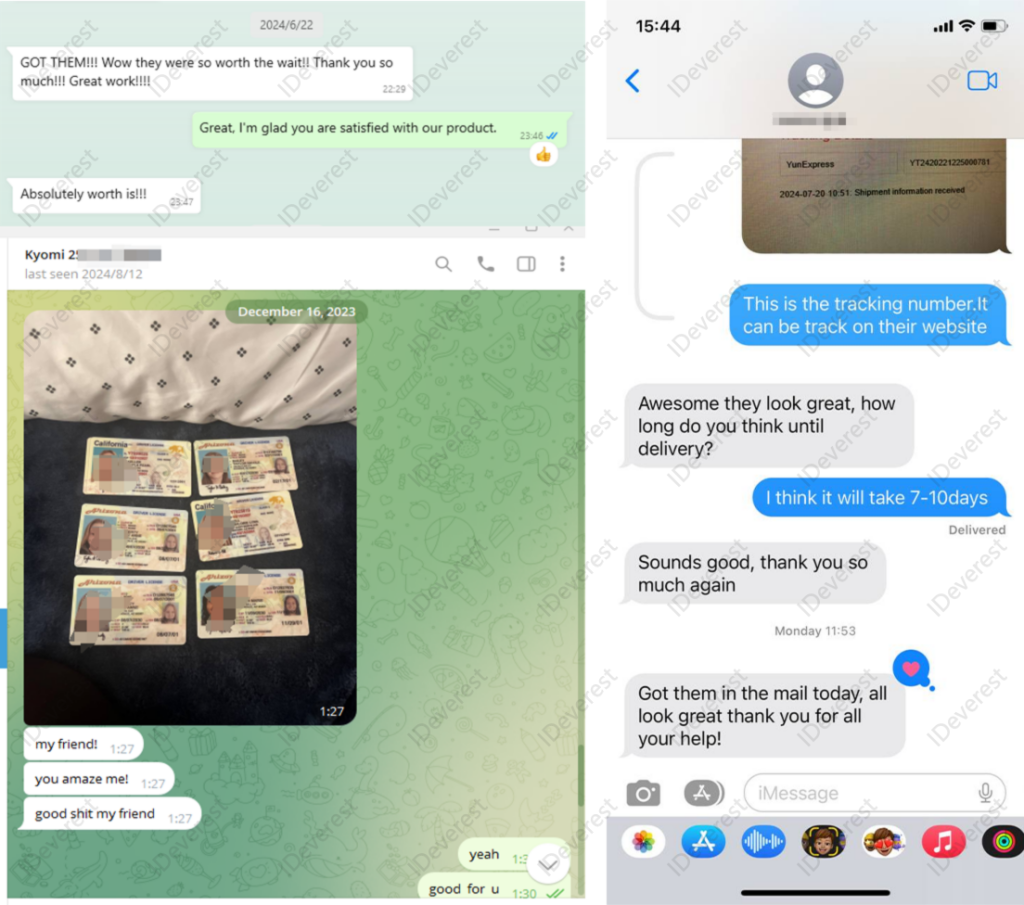





Big Treat Back for New Product Development Participation: Your feedback matters! We offer incentives to customers who participate in our new product development, shaping the future of our offerings together.

 Nebraska's New Driver's Licens
Nebraska's New Driver's Licens
 Advances in Technology Anti-Co
Advances in Technology Anti-Co
 What are the benefits of a fak
What are the benefits of a fak
 The development and history of
The development and history of